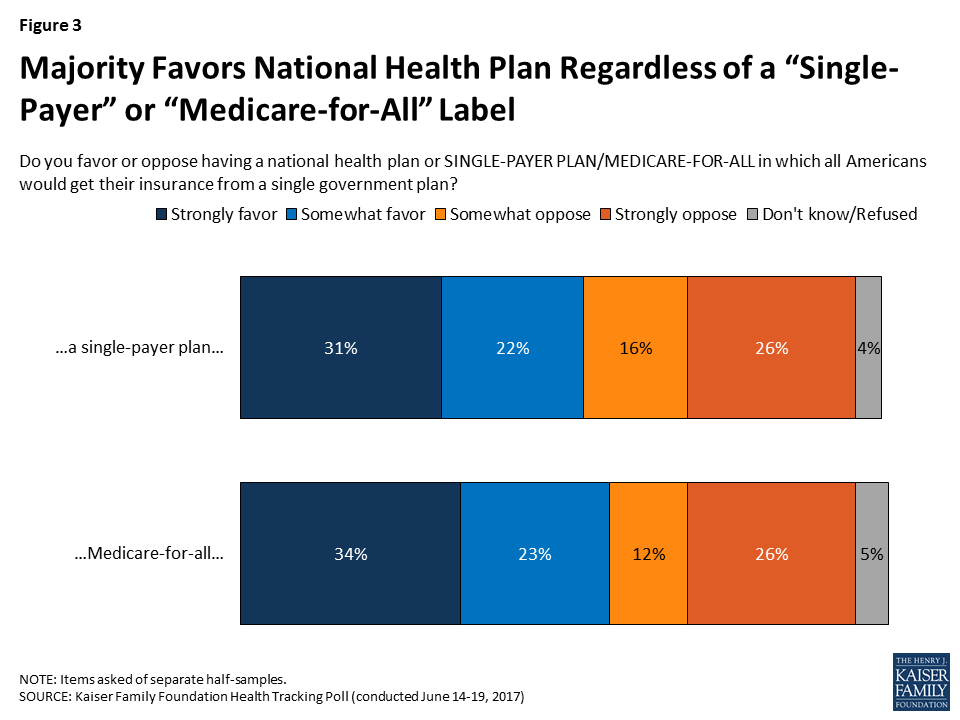
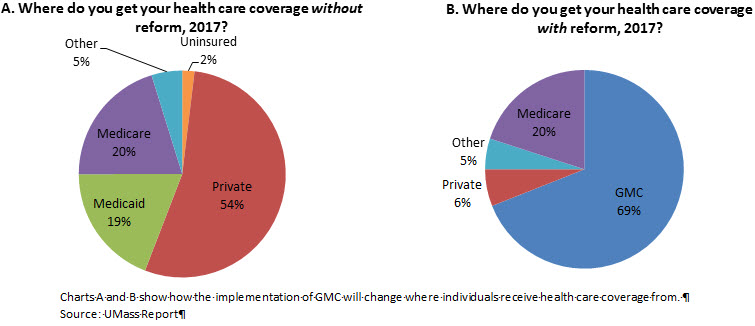
They can encourage healthy behaviors, but other elements exert higher influences on diet, exercise, sexual practices, alcohol and other substance abuse, and needle exchange practices (Woolf et al., 2011). Pediatricians can remind parents to secure their children in automobile seats, however they can not manage motor automobile crashes. Physicians can evaluate for and treat depression and look out for self-destructive ideation and indications of household violence but they have actually limited impact on the occurrence of guns or the social conditions that speed up crime and violence.
health Drug Abuse Treatment disadvantage to shortages in the public health or medical care system is that countries with much better health outcomes do not have constant evidence that their systems carry out much better. In some nations, clients are more most likely to report issues. For example, Sweden regularly ranks amongst the healthiest nations in the OECD, but, in the Commonwealth Fund surveys, its patients were most likely than U.S.
Sweden has high hospitalization rates for unchecked diabetes (Figure 4-4). In 2007, Switzerland had the greatest male life span amongst the 17 peer nations (see Table 1-3, in Chapter 1), however the accessibility of general specialists is the second least expensive (see Figure 4-1). Australia has the second highest male life span of the peer countries (see Table 1-3, in Chapter 1), but it has the 5th greatest case-fatality rate for ischemic stroke (OECD, 2011b).
Numerous prospective descriptions could account for these inconsistencies. The most basic is that medical care matters little to health, a thesis that some have actually advanced as part of a more basic argument that health is shaped mostly by the social and physical environment. Certainly, some research studies have currently questioned whether there specifies evidence to implicate the health care system as the reason for the U.S.
A second possibility is that health care does matter but that only specific elements impact outcomes. For instance, shortages in mammography screening or printing medication lists may not matter, and countries with consistently superior health outcomes might master the aspects of health care that are Drug Rehab Center substantial. Healthcare might likewise matter more in specific places or for particular patient populations.
Get This Report on A Health Care Professional Is Caring For A Patient Who Is About To Begin Taking Isoniazid
Longer life expectancy and enhanced health is most likely traceable to some mix of health system qualities and these other specific and neighborhood conditions, however the precise contribution of each aspect is unidentified and might differ over location and time. A life-course point of view adds extra complexity to the analysis since differences in health outcomes may relate not just to coexisting characteristics of health systems, Drug Rehab Delray but also to those that existed years earlier when current conditions or illness were developing.
For such conditions, shortages in primary care in the 1970s and 1980s might describe existing death rates much better than the functions of today's health systems. The existing health system matters more for care conditions that lead directly to health outcomes, such as birth outcomes and survival after an auto accident or gunshot injury.
health system may add to or ameliorate the U.S. health drawback. Equivalent international data for significant reasonings require much better data on both reliant (health results) and independent variables (health systems). Although information from the OECD and WHO offer some relative info on a handful of health system steps, these are just like the secrets under the lamppost.
Few indications for examining the different measurements of healthcare have been developed or undergone proper clinical validation. In specific, concerns utilized on studies such as those carried out by the Commonwealth Fund, which are extensively cited in this chapter, have unidentified correlations with health outcomes and may have variable meanings across nations - how much is health care.
Some concerns utilized by the Commonwealth Fund change from year to year; these modifications use new insights on health systems, however they make it tough to compare results throughout time. The Commonwealth Fund gives equivalent weight to each step; some weighting is most likely necessitated, however an empirical basis is lacking to understand which characteristics patients value more extremely or are more predictive of health results.
Some Ideas on Which Of The Following Is Not A Result Of The Commodification Of Health Care? You Need To Know
In the very first significant attempt to rank health care systems, the WHO World Health Report 2000 presented a ranking based upon health attainment, equity of health outcomes, "client responsiveness," and "fairness of financial contributions" (World Health Organization, 2000b). The U.S. health system ranked 37th based on this methodology, however the procedures, methods, and information were slammed (Jamison and Sandbu, 2001; Navarro, 2002).
In 2008, WHO identified five shortcomings in healthcare shipment that are found in systems around the globe: inverse care, impoverishing care, fragmented and fragmenting care, unsafe care, and misdirected care (World Health Company, 2008b). International health experts have actually not reached agreement on the ideal specifications for determining and tracking the performance of nationwide health systems.
The capacity of various countries to gather suitable data and to do so systematicallyusing constant sampling treatments, information collection techniques, coding practices, and measurement intervals (e. g., each year) is challenging for useful reasons and minimal budget plans. To cite simply one example, patient safety indicators for medical facility care are not standardized across nations (Drsler et al., 2012).
International surveys face methodological difficulties that present tasting biases. One example is study methodology: some surveys have utilized a combination of landlines and mobile telephones to perform interviews, and some nations have low action rates or mobile telephone usage. Adults with intricate conditions, low income, or language barriers might be undersampled.
The research study difficulties and concerns to address these gaps in the science are discussed further in Chapter 9, along with suggestions to correct the problem. Regardless of these limitations, the existing proof is certainly adequate for the panel to conclude that public health and medical systems in the United States have important shortcomings, a few of which seem more noticable in the United States than in other high-income nations. how did the patient protection and affordable care act increase access to health insurance?.
Fascination About How Did The Patient Protection And Affordable Care Act Increase Access To Health Insurance?
The difficulties Americans experience in accessing these services and getting premium care, as recorded in this chapter, can not be ignored as a prospective factor to the U.S. health drawback. 1Examples of main avoidance consist of smoking cessation, increased physical activity, administering immunizations to eliminate susceptibility to infectious illness, and helping individuals avoid damaging ecological exposures (e.
Secondary prevention consists of early detection of illness and danger consider asymptomatic persons (e. g., cancer and serum lipid screening). 2The larger public health system includes not just public health agencies, however likewise public and personal entities involved with food and nutrition, exercise, real estate and transport, and other social and financial conditions that impact health (Institute of Medication, 2011e).
3The same research studies estimate that in between 44 and 72 percent of the fall in death arised from a decrease in cardiovascular danger elements (smoking, lipids, and high blood pressure); see Chapter 5. 4Although a body of proof recommends that a large proportion of healthcare costs in the United States is related to squander and ineffectiveness (Berwick and Hackbarth, 2012), the high usage of healthcare resources might also be the product of the U.S.